I. Preface
The offset printing and gravure printing technologies established at the beginning of the 20th century provided a means to mass-produce prints at a high speed. Therefore, in a century, printing, publishing, news, and broadcasting became important roles for large-capacity media. However, the rapid changes in the social environment, such as the increase in the amount of information, the changes in quality, the digitization, and the rapid growth of computer networks, have also brought about tremendous changes in the printing industry. The diversification of lifestyles in personal life and the desire to express personality have changed the nature of the media and the flow of information, and it has begun to show a change from the original unidirectional personality to the dual direction. In the printing business, using the Internet, on-demand printing, which starts printing the compiled data in the required quantity, has started.
The printing industry so far has come as a huge equipment industry with the goal of improving productivity. In recent years, due to the digitization of information processing technology and the rapid development of hard copy technology, especially based on the technology that is fostered by family needs and business needs, inkjet and electrophotographic methods have promoted high resolution and high speed, and have sought to expand. Print on demand. In the printing market, we also promoted a short lead time and small batch production, a variable-printing printing press has emerged, digitization of printing peripheral devices and reorganization of high-speed data communication networks have prompted the realization of an on-demand printing environment. Formation. As an on-demand printer, various methods such as ink jet method and electrophotographic method have been developed. Prototype development is still underway. This is based on the principle of electrocoagulation, and introduces the "Elcography" digital printing machine without a plate. Technology.
Second, the development of the latitude and longitude of Elcography
Elcography began with A. Castegnier, a Canadian who originally worked in the photographic development business. He imagined whether or not he could use photographic printing paper to obtain photographic quality. Offset printing is undoubtedly unsuitable for printing one by one like a negative film. In 1971, A. Castegnier suddenly remembered the revelation of visiting the gravure rotary printing plant in Paris in 1951, and emerged to use bubbles that occur between electrodes of the yin and yang due to the electrolysis reaction. It is believed that the gelatin layer can form some intaglio ink holes. As long as ink is filled in the ink holes, it can be printed on plain paper (U.S. Patent No. 3,752,746). In fact, the occurrence of air bubbles is very unstable, and even if moisture evaporates to solidify the gelatin layer, problems such as sticking of the electrodes may occur, which cannot be realized as intended.
However, A. Castegnier, who has been passionate about this idea, founded Elcorsy in 1981 and devoted himself entirely to development. At the time, the dye ink had just been used for printing tests at a rate of 10 cm per second. By 1984, the basic idea of ​​Elcography was created. It was the use of synthetic resin colloids to induce electrochemical condensation between the electrodes to form images. (U.S. Patent 4,555,320).
Since then, the printing speed has been improved, the transfer effect has been improved, and multicolorization has begun. At the NEXPO exhibition in June 1996, Elcorsy and the Toyo Ink Corporation of Japan jointly published Elcography, at the 1998 IPEX exhibition. The Model 200 Elcography press was exhibited, printing full-color variable data at a printing speed of 200 dpi and 200 feet per minute. At the DRUPA 2000 exhibition, the Elco400 Digital press with a sub-division of 400 dpi was displayed. Every 400 feet. Currently, the two companies are developing new models that have improved the key parts of the press based on the Elco 400.
The main features of Elcography:
1) Use water-based ink, corresponding to VOC printing
2) High-speed printing at 400 feet per minute (120 meters per minute)
3) With 400dpi resolution
4) Reproducible 256 price adjustment
III. Image Formation Principle of Elcography
The original printing is that the ink itself does not cause any chemical changes to complete the formation of the image from the beginning to the end of the printing process (physical changes in the drying process accompanied by volatilization of the solvent). However, Elcography inks use the principle of electrochemical resin solidification, according to the data signal, to adapt to the current intensity flowing between the yin and yang electrodes, generate dots of corresponding size, and form images. The principle of electrocoagulation is derived from the surface of the metal anode water-soluble A chemical reaction between a functional group of a resin (polypropylene amide) and a trivalent iron ion. The resin contains a carboxyl group and a hydroxyl group, and when it is rendered water-soluble, it is accompanied by reactivity with iron ions.
Elco inks include components other than resins, pigments for pigmentation, dispersants for dispersion of auxiliary pigments, and chloride salts for improving conductivity.
Anode passivation layer
The image-creating electrode is formed of a metal anode covered with a passivation layer and a tip cathode arranged perpendicular to the anode, filled with Elco ink (see FIG. 1).
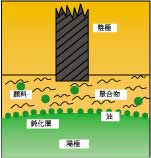
Elcography electrodes
The non-Kinxiu steel used on the anode of Elcography has the property of forming a so-called self-passivation state, is easily oxidized, and forms a thin passivation layer of several angstroms (A) which is chemically or electronically inert on its surface. When this layer is subjected to compulsive damage, in the presence of oxygen, a new passivation layer can be easily regenerated.
The anode of Elcography is in the shape of a roller, with a gap of about 50 μm, and the cathode is arranged opposite to the roller. As the anode roller rotates, the ink is injected into the gap between the electrodes.
2. Cathode activation and destruction of passivation layer
When the current does not flow between the electrodes, it is inert and does not cause any change. Once the cathode is given a direct current pulse corresponding to the image data, the charge will initiate the electrolysis of the chlorine aqueous solution, and the chlorine contained in the ink will locally destroy the anode surface opposite to the cathode. The passivation layer activates the anode surface. After activation, the amount of ferric iron ions in the length of the pulse should be eluted into the ink (see Figure 2 and Figure 3).


Cathode activation Metal ions elution
3. Agglomeration of the Resin The eluted iron ions react with the carboxyl phase of the water-soluble resin dissolved in the ink, and the pigment particles dispersed in the ink are drawn while being drawn to form a solidified body. Finally, a colored dot is formed. The amount of solidified resin is proportional to the amount of iron ions that elute, and the length of the current pulse can be adjusted according to the image data, so that the amount of solidified resin can be controlled. (Continued from the next issue...)
Pallet Slip Sheet,Paper Slip Sheet,Plastic Slip Sheet Pallet,Plastic Sheets For Slip
DONGGUAN YEE HUP TRADING CO,.LTD , https://www.yeehupack.com